Getting started with HDF5 widgets#
Silx provides an implementation of a tree model and a tree view for HDF5 files. The aim of this tree is to provide a convenient read-only widget supporting file formats often used in synchrotrons for big amounts of data.
This page displays some source code to explain how to use this widget.
Commented source code#
Import and create your tree view#
HDF5 widgets are all exposed by the package silx.gui.hdf5.
import silx.gui.hdf5
treeview = silx.gui.hdf5.Hdf5TreeView()
Custom your tree view#
The tree view can be customised to be sorted by default.
# Sort content of files by time or name
treeview.setSortingEnabled(True)
The model can be customised to support mouse interaction.
A convenient method, i.e., Hdf5TreeView.findHdf5TreeModel(), returns the main
HDF5 model used through proxy models.
model = treeview.findHdf5TreeModel()
# Avoid the user to drop file in the widget
model.setFileDropEnabled(False)
# Allow the user to reorder files with drag-and-drop
model.setFileMoveEnabled(True)
The tree view is also provided with a custom header that helps to choose visible columns.
header = treeview.header()
# Select displayed columns
column_ids = [treeview.findHdf5TreeModel().NAME_COLUMN]
header.setSections(column_ids)
# Do not allow the user to custom visible columns
header.setEnableHideColumnsPopup(False)
Add a file by name#
The model can be used to add an HDF5 file. It is internally using
silx.io.open().
model.insertFile("test.h5")
Add a file using h5py#
The model internally uses the h5py object API.
We can use directly h5py Files, Groups and Datasets.
import h5py
h5 = h5py.File("test.h5", mode="r")
# We can use file
model.insertH5pyObject(h5)
# or group or dataset
model.insertH5pyObject(h5["group1"])
model.insertH5pyObject(h5["group1/dataset50"])
Add a file using silx#
Silx also provides an input API and supports HDF5 files through h5py.
import silx.io
# We can load HDF5 files
model.insertH5pyObject(silx.io.open("test.h5"))
# or Spec files
model.insertH5pyObject(silx.io.open("test.dat"))
Capture selection#
The Hdf5TreeView widget provides default Qt signals inherited from
QAbstractItemView.
- activated:
This signal is emitted when the item specified by index is activated by the user. How to activate items depends on the platform, e.g., by single- or double-clicking the item, or by pressing the Return or Enter key when the item is the current one.
- clicked:
This signal is emitted when a mouse button is clicked. The item selected by mouse click is specified by index. The signal is only emitted when the index is a valid one.
- doubleClicked:
This signal is emitted when a mouse button is double-clicked. The selected item is specified by index. The signal is only emitted when the index is a valid one.
- entered:
This signal is emitted when the mouse cursor enters the item specified by index. Mouse tracking needs to be enabled for this feature to work.
- pressed:
This signal is emitted when a mouse button is pressed. The selected item is specified by index. The signal is only emitted when the index is a valid one.
The method Hdf5TreeView.selectedH5Nodes() returns an iterator of H5Node
objects which wrap h5py objects adding extra information.
def my_callback(index):
objects = list(treeview.selectedH5Nodes())
obj = objects[0] # for single selection
print(obj)
print(obj.basename) # not provided by h5py
print(obj.name)
print(obj.file.filename)
print(obj.local_basename) # not provided by h5py
print(obj.local_name) # not provided by h5py
print(obj.local_file.filename) # not provided by h5py
print(obj.attrs)
if obj.ntype is h5py.Dataset:
print(obj.dtype)
print(obj.shape)
print(obj.value) # create a copy of data of the dataset
print(obj.h5py_object) # reference to the Hdf5 dataset (or group)
treeview.clicked.connect(my_callback)
Example#
The hdf5widget.py sample code provides an example of properties of the view, model and header.
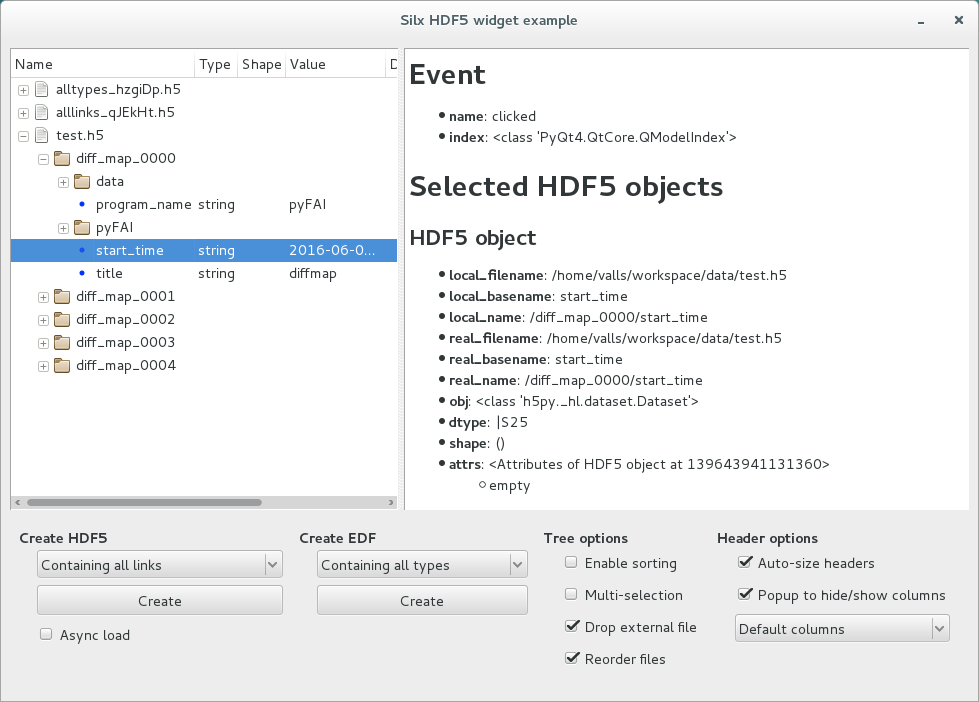
Source code: hdf5widget.py.
After installing silx and downloading the script, you can run it from the command line prompt:
python hdf5widget.py <files>
This example loads files added to the command line, or files dropped from the file system. It also provides a GUI to display dummy test files.
