Getting started with HDF5 widgets¶
Silx provides an implementation of a tree model and a tree view for HDF5 files. The aim of this tree is to provide a convenient read-only widget supporting file formats often used in synchrotrons for big amounts of data.
This page displays some source code to explain how to use this widget.
Commented source code¶
Import and create your tree view¶
HDF5 widgets are all exposed by the package silx.gui.hdf5.
import silx.gui.hdf5
treeview = silx.gui.hdf5.Hdf5TreeView()
Custom your tree view¶
The tree view can be customised to be sorted by default.
# Sort content of files by time or name
treeview.setSortingEnabled(True)
The model can be customised to support mouse interaction.
A convenient method, i.e., Hdf5TreeView.findHdf5TreeModel(), returns the main
HDF5 model used through proxy models.
model = treeview.findHdf5TreeModel()
# Avoid the user to drop file in the widget
model.setFileDropEnabled(False)
# Allow the user to reorder files with drag-and-drop
model.setFileMoveEnabled(True)
The tree view is also provided with a custom header that helps to choose visible columns.
header = treeview.header()
# Select displayed columns
column_ids = [treeview.findHdf5TreeModel().NAME_COLUMN]
header.setSections(column_ids)
# Do not allow the user to custom visible columns
header.setEnableHideColumnsPopup(False)
Add a file by name¶
The model can be used to add an HDF5 file. It is internally using
silx.io.open().
model.insertFile("test.h5")
Add a file using h5py¶
The model internally uses the h5py object API.
We can use directly h5py Files, Groups and Datasets.
import h5py
h5 = h5py.File("test.h5")
# We can use file
model.insertH5pyObject(h5)
# or group or dataset
model.insertH5pyObject(h5["group1"])
model.insertH5pyObject(h5["group1/dataset50"])
Add a file using silx¶
Silx also provides an input API and supports HDF5 files through h5py.
import silx.io
# We can load HDF5 files
model.insertH5pyObject(silx.io.open("test.h5"))
# or Spec files
model.insertH5pyObject(silx.io.open("test.dat"))
Capture selection¶
The Hdf5TreeView widget provides default Qt signals inherited from
QAbstractItemView.
- activated:
This signal is emitted when the item specified by index is activated by the user. How to activate items depends on the platform, e.g., by single- or double-clicking the item, or by pressing the Return or Enter key when the item is the current one.
- clicked:
This signal is emitted when a mouse button is clicked. The item selected by mouse click is specified by index. The signal is only emitted when the index is a valid one.
- doubleClicked:
This signal is emitted when a mouse button is double-clicked. The selected item is specified by index. The signal is only emitted when the index is a valid one.
- entered:
This signal is emitted when the mouse cursor enters the item specified by index. Mouse tracking needs to be enabled for this feature to work.
- pressed:
This signal is emitted when a mouse button is pressed. The selected item is specified by index. The signal is only emitted when the index is a valid one.
The method Hdf5TreeView.selectedH5Nodes() returns an iterator of H5Node
objects which wrap h5py objects adding extra information.
def my_callback(index):
objects = list(treeview.selectedH5Nodes())
obj = objects[0] # for single selection
print(obj)
print(obj.basename) # not provided by h5py
print(obj.name)
print(obj.file.filename)
print(obj.local_basename) # not provided by h5py
print(obj.local_name) # not provided by h5py
print(obj.local_file.filename) # not provided by h5py
print(obj.attrs)
if obj.ntype is h5py.Dataset:
print(obj.dtype)
print(obj.shape)
print(obj.value) # create a copy of data of the dataset
print(obj.h5py_object) # reference to the Hdf5 dataset (or group)
treeview.clicked.connect(my_callback)
Example¶
The hdf5widget.py sample code provides an example of properties of the view, model and header.
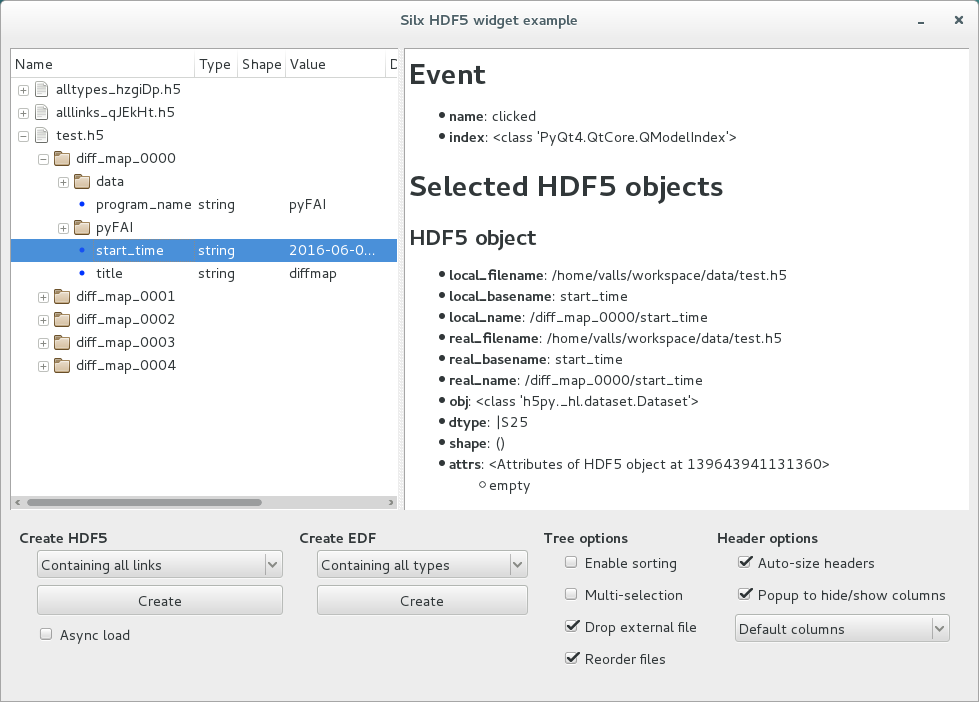
Source code: hdf5widget.py.
After installing silx and downloading the script, you can run it from the command line prompt:
python hdf5widget.py <files>
This example loads files added to the command line, or files dropped from the file system. It also provides a GUI to display dummy test files.
